What are the different types of automotive oil additives?
How do they work?
Let’s try to tell you about it in simple, accessible language. There are many different additives in oil to improve the operation of car units – engine, gearbox, power booster, gearbox, etc. The principle of their action is absolutely different.

The basic idea of their action is to place something intermediate between the rubbing surfaces, so that the steel surfaces rub not against each other, but through an intermediate, more slippery material.
Different materials can act as such a layer.
Initially, at the very beginning of the development of mechanical engineering, grease, tar, coal dust, etc. were used. All this was designed to reduce friction between the rubbing pairs of parts.
There are different means that promise victory over the wear of rubbing surfaces, victory over friction, increase the life of parts and mechanisms. All of them work differently.
Parts have surfaces at the micron level that are not smooth. They have ridges and depressions. This is called roughness.
When measured, you can see that the surface of machined car engine parts, have ridges and depressions at about five microns, depending on the degree of surface finish.
The depressions are good because they can hold oil, to reduce friction on the parts. The oil is buried in the depressions and is distributed and held on the surface by surface tension.
The protrusions, on the other hand, allow the oil to run off. And it is the ridges on the surface that are responsible for the wear of parts and rubbing surfaces. Because when two parts meet and interact with each other, they affect each other with protrusions.
In these protrusions, there is a situation with very high temperatures and pressure in this small local point of contact between the protrusions. Such catastrophic conditions are created there that the metal is destroyed. The metal in such points becomes very hot and soft. And under the influence of pressure and friction, it breaks down. This process is wear.
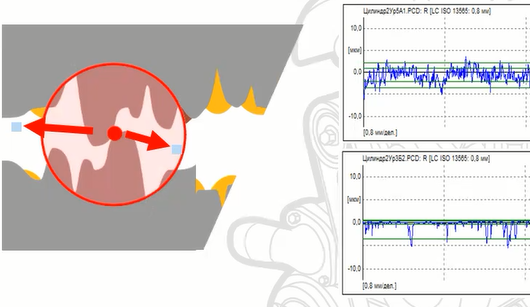
Let us consider the action of additives in oil on the example of automobile engine operation.
The main technologies that are now used in the production of engine oil additive we will describe below.
We will deliberately not name manufacturers, trademarks or use other advertising tricks. The composition of engine oil additive usually the manufacturer writes on the package and you can easily navigate in the sea of trade offers.
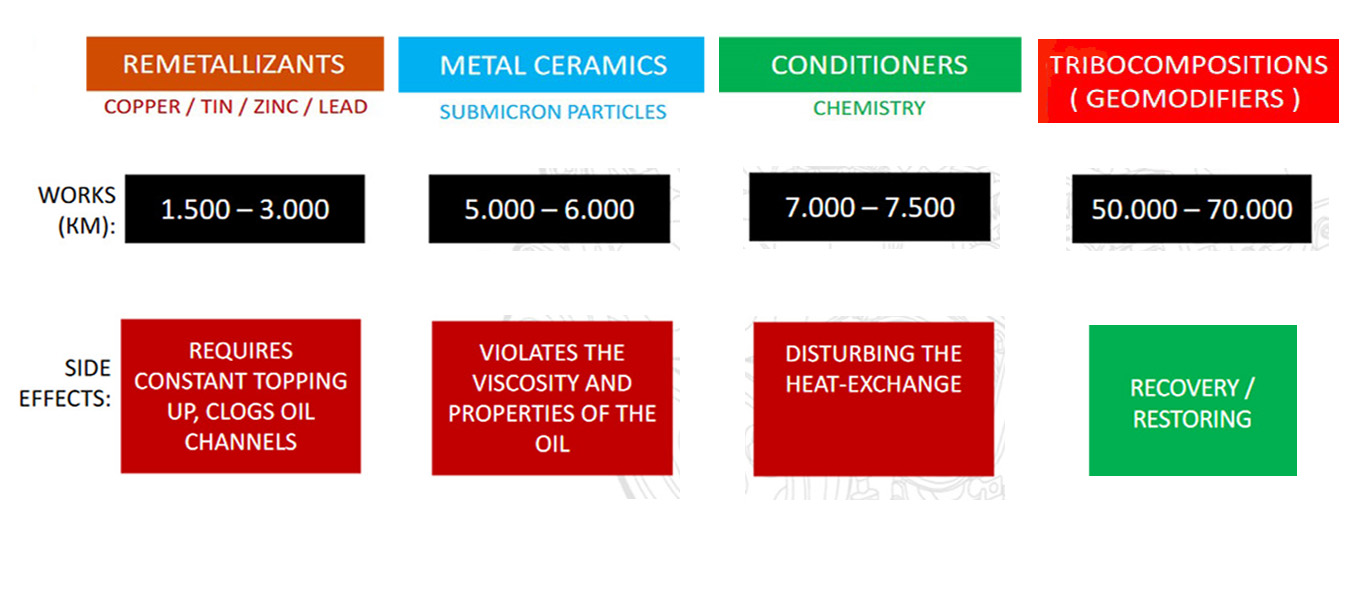
The whole history and evolution of friction solution came to the following classification of friction-reducing technologies.
5. Tribocompositions or tribotechnical compound

Oil modifiers are an actively used friction reduction technology.
The technology directly changes the properties of the oil – viscosity, cleaning properties, etc. However, one can never say for sure how the oil will interact with such a modifier.
Oil producers independently select the optimal properties for engine oil. But there are manufacturers who offer their own improvements to the traditional oil.
Oil modifiers, which are added to oil to solve urgent problems here and now, are an exception. For example, eliminating oil leaks in rubber seals and oil seals, or emergency oil pressure drop, etc. Manufacturers advise their use in emergency cases, when it is not possible to make a scheduled repair. Since the oil properties change significantly.
Remetallizants are antifriction additives for machine oil.
This technology appeared at the beginning of the 20th century. Then people realized to add copper dust between rubbing pairs of parts.
Tin, zinc, lead and other metals were and are also used. Soft metal dust is added to engine oil. They are fusible and have a very small coefficient of friction.
If this dust gets into the engine, where there is high temperature and high pressure, it is distributed into a thin film. This thin film acts as a slippery surface through which the parts of the engine or gearbox or any other mechanism friction occurs.
Friction is reduced, hence power is increased. And it gives the impression that the unit, such as an engine, has recovered. It spins more easily. Driving becomes more dynamic, fuel is consumed less.
However, no soft metal can restore steel. These metals have different crystal lattices and properties. This is a temporary effect, which has its side effects.
After 1500 – 3000 km the effect of the additive actually stops.
In our opinion, it is an ideal additive when you need, for example, to sell your car. Yes, yes, exactly so! The buyer will get a well working engine at the time of the deal. The car can be sold profitably. And what will happen to the car will be the problem of the new owner.
Every 1500 – 3000 km you need to buy a can of such additive again to prolong the effect.
When disassembling such an engine, you can see that all the insides with a surface layer of copper. This is due to the fact that copper has a positive charge, and the engine is negative. Thus, the copper is distributed, sticks to the inner surface of the engine.
Such additives are quickly triggered and stop working. And, most importantly, clog the oil channels in the mechanisms, settle inside. This can lead to the impossibility or difficulty of oil flow into the friction area, which can even lead to jamming of the engine or any other mechanism. Such cases can be found on the Internet.
Metal Ceramics is a technology that emerged after remetallizants.
In fact, it is a modernization of remetallizants. These are ultra-small submicron ceramic particles with boron nitrite and other materials that are added to the oil to deliver these particles to the rubbing pairs of machinery parts.
In those parts of the rubbing surfaces where pressure and temperature are high, a ceramic film is created. Ceramics have a low coefficient of friction.
There is virtually no coefficient of friction when friction is applied to ceramics. The surfaces are very slippery.
But this construction has its negative properties. Metal ceramics is brittle. And the engine has thermal expansion and thermal contraction. When heating the metal expands, the gap between the rubbing surfaces increases, and when cooling the metal shrinks, the gap decreases. And due to these effects metal ceramics loses its original effect on the friction process. The surface layer splits, fragments. Heat dissipation from the friction surfaces is impaired.
Metal ceramics acts on the engine up to 5000 – 6000 km of mileage, in spite of the often much more exaggerated effect of such engine oil additive declared by the manufacturer. To continue the effect it is necessary to repeat the purchase of such engine oil additive every 5000 – 6000 km of mileage to reduce friction again and continue the effect. Is it possible to call such a solution economical?
Also with the constant use of metal ceramics and with a mileage of 100 000 – 150 000 km the internal cavities of the engine block are clogged with metal ceramics. This leads to the same problems as with the use of remetallizants – clogged oil channels, which leads to the impossibility or difficulty of oil flow into the friction area, jamming of the engine, or increased wear of the rubbing surfaces. Described examples among users to find on the Internet is also not difficult.
In addition, metal ceramics is a heat insulator, and its uneven distribution leads to constant overheating of the engine, and as a consequence, to the replacement of the engine block. When disassembling the engine, which was constantly poured metal ceramics, you can see the chaotic buildup of metal ceramics in the cavities and recesses. And it is not always possible to remove it.
Metal Conditioners are the next friction reduction technology.
In areas where there is a higher probability of deformation from uneven oil distribution, when oil pressure is low, especially during cold engine starts or in traffic jams, the metal conditioner forms a protective film on the metal and protects the rubbing surfaces.
This will reduce friction nicely.
But metal conditioner must be added to the oil in large quantities, more than 70ml per liter of machine oil. That’s about more than 200ml of chemical compounds to the volume of engine oil that the car manufacturer recommends. That’s a lot of stuff. This ultimately affects the properties of the oil, changes it.
In addition, metal conditioner works quickly in urban environments. The action of metal conditioner extends to a mileage of up to 7000 -75000 km.
After that, the car is left with oil with changed characteristics and metal conditioner that does not work. Demanding and attentive drivers think about the need to change the oil and again pour a new can of metal conditioner to continue the effect. This is expensive. It takes a lot of time.
Metal conditioner works well when driving on highways at high speeds. In urban conditions, its effectiveness is reduced.
So far we have looked at the technologies that are used by different engine oil additives manufacturers around the world.
But there is another technology that is used by only one engine oil additives manufacturer. Due to the fact that it is somewhat exclusive technology we will dwell on it in more detail.
The above-mentioned technologies are used to varying degrees by such manufacturers as Liqui Moly, Xado, Sea foam, Lucas and others… You can see their rating here.
Now let’s try to understand the new and most promising technology. What companies use it, and how it differs from the technologies of older generation of production.
Tribocompositions (tribotechnical compound) – The distinctive feature of tribocompositions is that it does not separate the rubbing surfaces. It is not a gasket between rubbing pairs of parts. Its chemical composition is neutral to oil and does not change its properties. Its effect is observed during 50000-70000km of mileage. This is an absolute record among engine oil additives.
Tribocompositions form conditions for the formation of metal protective surface on the parts. From micro-particles of metal, of which the unit itself, engine, or gearbox, etc. is made of. The geometry of rubbing pairs of parts is restored. There is a restoration of working surfaces.
The friction surface becomes finely porous, which retains oil very well. So well that you can notice an interesting fact on the surfaces of engine parts. You can feel an oil film to the touch, but it is very difficult to wipe off this oil film. The only way to deal with it is with a large dose of solvent.
After application of tribocompositions, compression is restored, fuel consumption is reduced, excessive vibration in the car is eliminated, cold starting of the engine is facilitated, oil consumption is significantly reduced and oil combustion is practically stopped, etc.
Other additives affect only friction, reduce it, but there is no restoration of parts.
There are 2 components in tribocompositions. Pure base oil without chemistry, modifiers and other things, which acts as a carrier of active mineral with a size of about 1 micron. The composition of minerals used in tribocompositions is kept secret and is the manufacturer’s know-how, it is the result of many years of research by a scientific research center and leading industry experts.
These minerals are characterized by special natural properties. When they get into the stressed points of interaction of rubbing surfaces with high temperature and pressure, they affect the hardness of the parts. And the surface, instead of losing metal in the interaction on the contrary, captures and attracts metal particles from the surrounding space.
So the wear process stops. And the process of surface regeneration starts.
This process is repeated many times and a continuous protective metal layer is formed. As a result, all the damages that were on the friction surface – scoring, depressions, etc. – grow back. And the surface becomes as good as new and even better.
An important feature – in the gaps between the metal particles, which, as it were, welded to the restored surface, there are a lot of all sorts of small voids. They are called micropores.
Oil penetrates into these micropores and is perfectly retained in them. Thus, oil forms a single oil film on the entire surface of the rubbing parts and mechanisms.
Treatment of tribocompositions yields two effects.
The first is that the roughness of the parts is filled with metal particles and the gaps between the rubbing surfaces become smaller. They are optimized. For example, if we had scoring and depressions, through which, for example, gases burst in the cylinder, compression and engine power fell, now these channels are filled with metal particles and the problems associated with this are solved.
Secondly, a perfect oil film is formed on the surface. Which does not disappear from the surface, does not flow into micro depressions, does not leak excess into the combustion chamber of the engine.
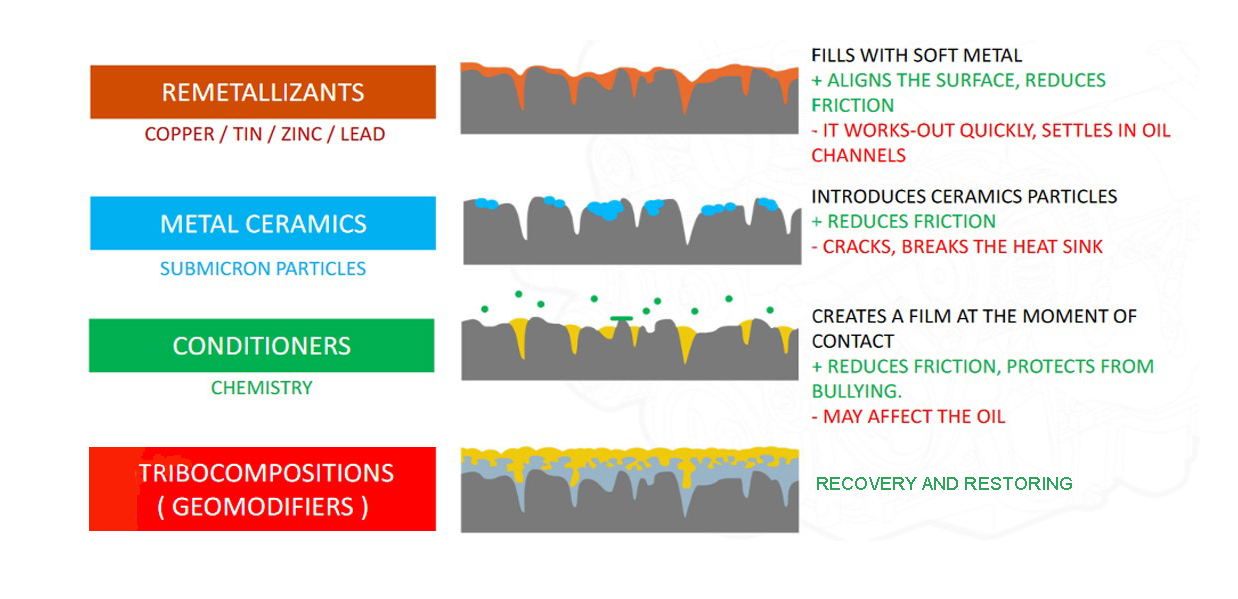
This effect of tribocompositions helps the oil to fulfill its functions very much. As a result, there is a significant improvement in the performance of the unit – engine, gearbox, gearbox, power steering mechanism, etc. Wherever tribocompositions are used there is a qualitative change.
This is such an interesting technology.
We managed to find the only manufacturer in the world that uses this technology. This is the Atomium brand.
Dear readers, if you have your own experience of using engine oil additives write us. All information for this article was taken from public sources.
In the future we will continue to share our experience of using engine oil additives.
Good luck on the road!






